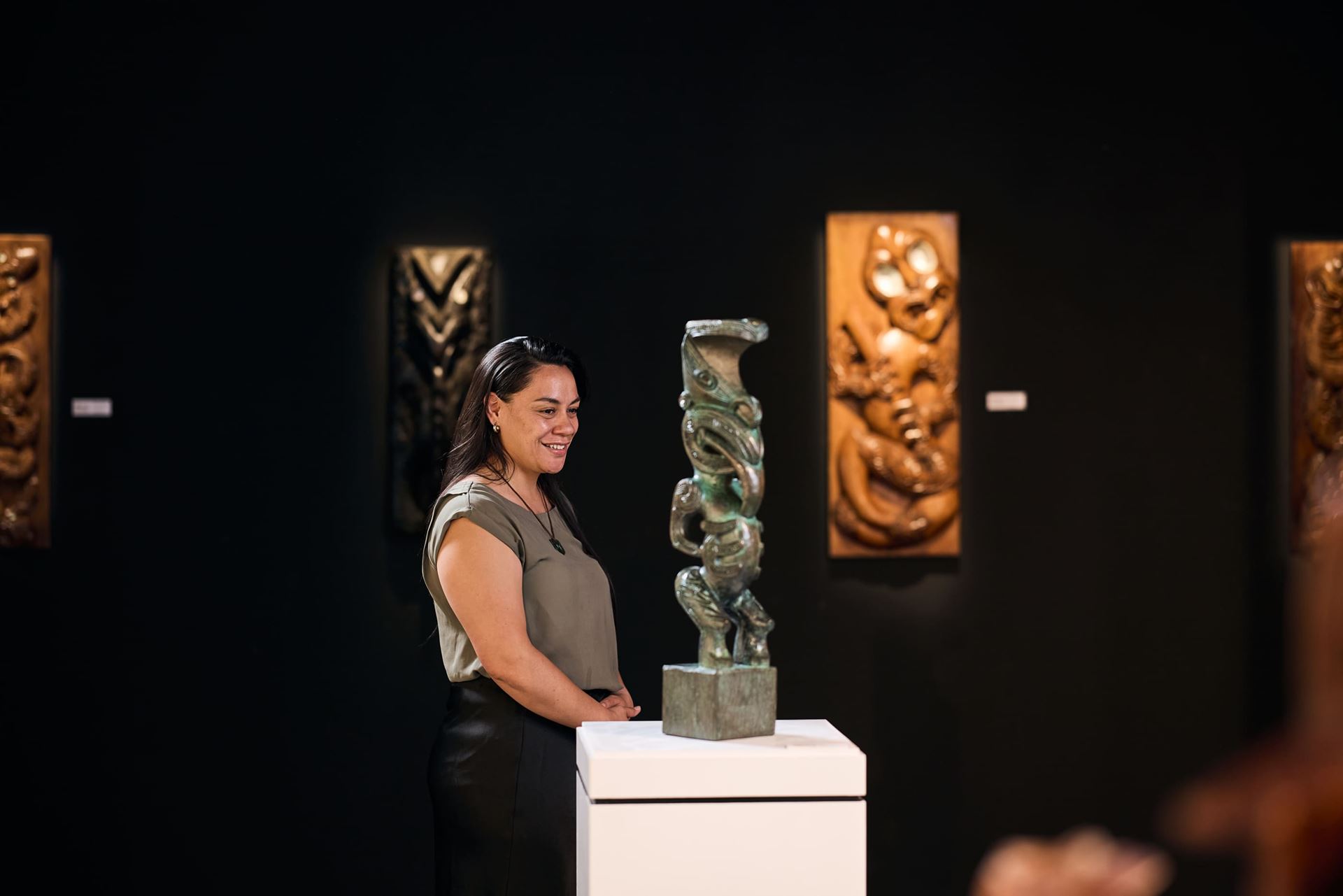
Whakakōhatu - Bronze & Resin
Te Ahi Komau was our Foundry area at the New Zealand Māori Arts & Crafts Institute where bronze and resin casts were made.
Bronze Hoe
The paddle or hoe was the means of propulsion for the Māori waka (canoe). While the hoe was primarily a paddle, it also doubled as a weapon when the need arose. Carved paddles were the property of the chief and were highly valued. The hoe came in different styles and the handles and blades differed from area to area.
$45,000.00
Pāpaka (ed. 2/12) - 4080FD
Pāpaka (crab catching stick) originated in Hawaiki (the original homeland of Māori). Rēhua (the god of fish) handed a pāpaka to a rangatira (chief) before his journey to Aotearoa. This pāpaka is part of a limited edition of 12 bronze casts from an original wood carving by Kawana Waititi. The original will remain part of the New Zealand Māori Arts and Crafts Institute legacy collection.
$3,900.00
Wahaika - Black w Bronze (ed. 1/6) - 2487FD
The literal meaning of wahaika is: ‘waha’ (mouth); and, ‘ika’ (fish). It was specifically named because of the gap on the side of the weapon. Wahaika were used in close hand-to-hand combat to defect blows, and to strike the chest, head and wrist. Many wahaika have a small figure carved on their side called a pūkaiora which represented a tribal war God that would guard over the warrior during battle. The whiti or small head at the end of the handle was also a form of guardian. Wahaika are usually made from native hardwoods or whalebone.
$7,500.00